The Different Types of Body Fat
17th Aug 2024
Which Fats Are Good, Which to Avoid and How They Affect Your Body
Have you ever wondered about the types of fats in your body?
What about the different types of belly fat and how to get rid of it?
This article will go over the difference between fat in your body, the ideal fat distribution types and how to get rid of fat.
Jump there now:
- What is Visceral Fat and Subcutaneous Fat?
- How Do I Know If My Belly Fat is Visceral or Subcutaneous?
- How Much Visceral and Subcutaneous Fat Should I Have?
- How to Lose Visceral Fat
- Types of Fat – Dietary Fat
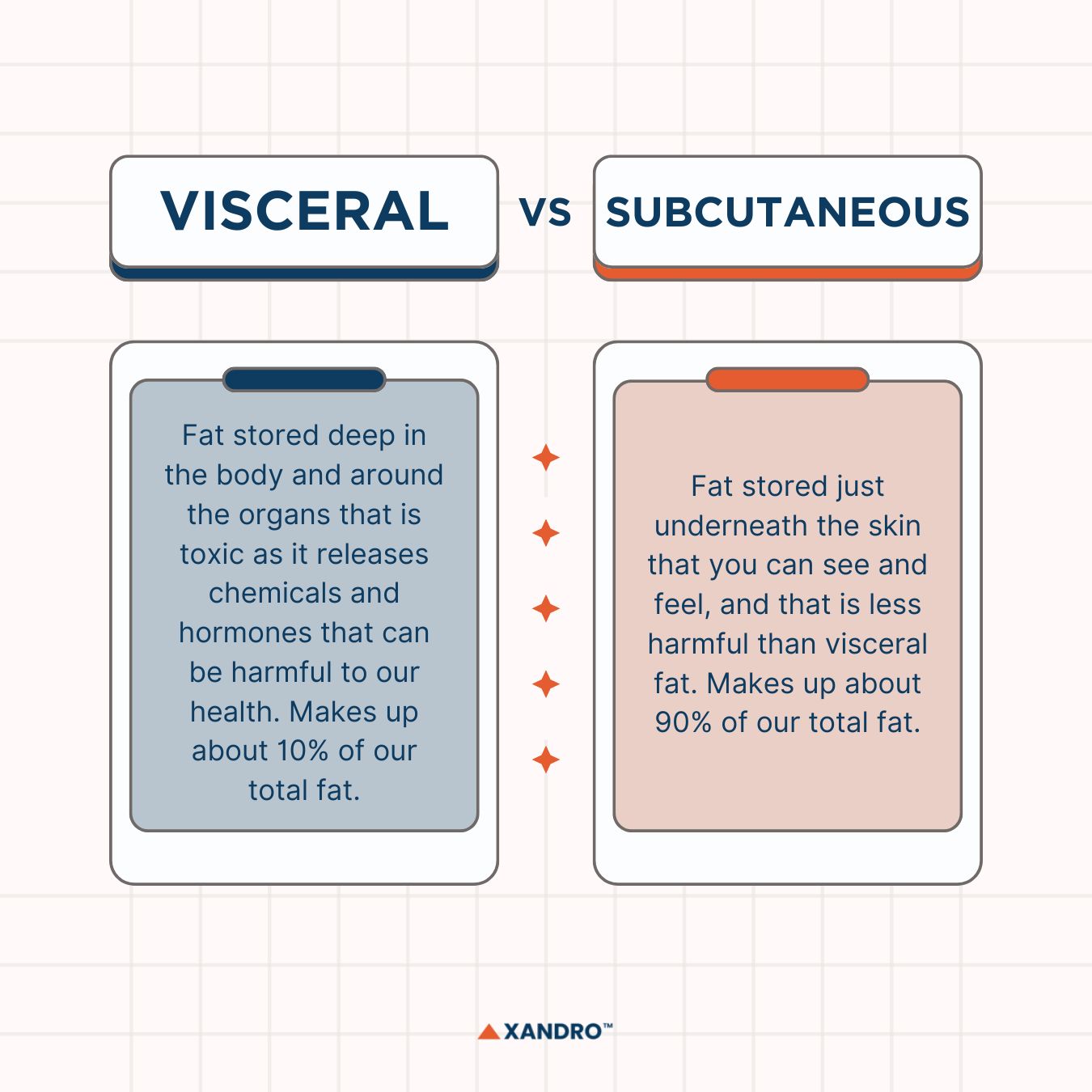
Visceral fat is the fat stored deep inside the body, such as in your abdomen and around your internal organs like the heart, liver and intestines. It’s also known as toxic fat as it makes chemicals and hormones that can be toxic to the body, so it can be more harmful to your health compared to subcutaneous fat. Those who carry more visceral fat, which is actually more common in males than females, have a higher chance of various health risks, such as:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Dementia
- Asthma
- Breast cancer
- Colorectal cancer
Subcutaneous fat, on the other hand, is the fat stored just underneath the skin — the fat that we see and can feel.
What is good, visceral or subcutaneous fat? Neither type of fat is ‘good’ as you shouldn’t have too much of either, but visceral fat is the one you should keep to a minimum.
Visceral fat occurs when we eat too many calories and don’t do enough physical activity, and the fat gets stored in the body. Men, women in menopause, people who had a low birth weight and those who drink too much are at a higher risk of storing visceral fat. It can also be due to genetics.
What are the 3 types of fats? Visceral and subcutaneous fat is the location of the fat, but fat is categorised as either brown fat, white fat or beige fat. We talk all about the difference between brown and white adipose fat/tissue here.
You can get a general idea if you have visceral fat by measuring your waist, as your waist circumference can give you an indicator of how much fat is around your organs and deep inside your belly.
Your risk of chronic diseases is higher if your waist circumference is larger than:
- Visceral fat range female: over 80cm
- Visceral fat range male: over 94cm
While BMI isn’t the most conclusive health determiner, it may help you determine if you’re in a healthy weight range for your height. You can find BMI calculators online.
You do need some levels of visceral fat to help protect your organs but too much can be dangerous for your health.
Visceral fat should make up about 10% of your body fat but if your body fat percentage is higher than recommended, this means your visceral fat will be, too.
The same is true with subcutaneous fat. You need some to help protect your body as it adds padding to your muscles and bones to protect you from falls and helps control your body temperature.
Subcutaneous fat generally makes up around 90% of your body fat.
Further Reading: Ultimate Guide to Weight Management
If you are above a healthy weight range, the best way to reduce visceral fat is by losing weight and by eating a healthy diet. Here are some tips:
- Eat a healthy diet: Eat plenty of lean protein, whole grains, fruits, vegetables and low-fat dairy, while limiting trans fats, excess sugar and salt as well as processed foods.
- Exercise: Exercise for at least 30 minutes a day, including cardio and strength training.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for at least seven hours of sleep a night, especially since not enough sleep may increase your risk of visceral fat.
- Reduce stress: Stress activates cortisol, a hormone in the body that triggers the storage of visceral fat.
- Limit alcohol: Drinking excess alcohol may increase your body’s visceral fat.
- Try intermittent fasting: This weight loss strategy may help reduce levels of visceral fat.
Further Reading: Spermidine to Help Your Intermittent Fasting Efforts
As for how to lose subcutaneous fat, these same strategies will help you.

Is it easier to lose visceral or subcutaneous fat?
Subcutaneous fat is harder to lose than visceral fat. Visceral fat metabolises quicker and your body also gets rid of it as sweat and pee. If you persist in exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet, you should notice a difference within two to three months.
Signs you are losing visceral fat include:
- A reduced belly
- A reduced waist size
- You notice your clothes fit differently, even if the scales stay the same
- Your body feels healthier due to the changes in your diet and from exercise
- You’re snoring less
- Your blood pressure is lower
Further Reading: Supplements for Weight Loss
Now that you know about fat in the body, what are the 4 different types of fats that we consume through food?
As mentioned, we all need a small amount of fat in our bodies and to have a healthy diet, which we get through the foods we eat. These are categorised into four types:
- Monounsaturated fats
- Polyunsaturated fats
- Saturated fats
- Trans fats
Unsaturated fat vs saturated fat
Saturated fats are commonly found in meats and dairy and are usually solid at room temperature while unsaturated fats are found in vegetable oils, nuts and fish and are usually liquid at room temperature.
But which fat is good, saturated or unsaturated? Unsaturated. This is broken down into two, known as monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats, which are known as ‘healthy’ fats as they help us maintain healthy cholesterol (the fatty substance in your blood) levels.
What type of fat should I avoid? You should limit the amount of saturated and trans fat foods you consume in your diet as these are ‘unhealthy’ fats that raise your bad, or non-HDL, cholesterol, which can increase your risk of stroke and heart attack.
Types of fat foods
- Types of unsaturated fat foods:
- Monounsaturated: nuts, like almonds, cashews, pistachios, hazelnuts, peanuts and peanut butter, olive oil, olives and avocados.
- Polyunsaturated: oily fish, like salmon and mackerel, sunflower oil, rapeseed oil, walnuts, pine nuts, sunflower seeds and sesame seeds.
- Types of saturated fat foods: processed and fatty meats such as bacon, ham and sausages, hard cheeses, whole milk, cream, butter, ice cream, lard, palm oil and coconut oil.
- Types of trans fat foods: fried foods, biscuits, cakes, pies, pastries and margarine.
End Note
While we all need some fat in our diets and bodies, it’s important to focus on eating healthy fats and limiting unhealthy fats, as well as on exercising regularly and making healthy lifestyle choices to reduce the amount of fat in our bodies.
When looking into weight management strategies, make sure to speak with your doctor beforehand to ensure you’re implementing the right strategies to develop healthy, long-term habits.
Looking to help your weight loss goals? Xandro Lab’s Lean XP helps burn off visceral belly fat and boost your metabolism. Read what people are saying about it and how it can help you achieve your long-term goals!
