What is Glycine Good For? Benefits, Uses and Side Effects
22nd Jul 2025
What Is Glycine and What is Glycine Used For?
Glycine is a simple amino acid that plays many important roles in the body. It helps produce serotonin, a hormone that boosts mood, supports nerve signal transmission and helps with detoxification.
Glycine is also a major component of collagen, the protein that provides structure to bones, skin, muscles and connective tissues. While the body can produce glycine naturally, it is also found in certain foods and available as a supplement.
Research suggests glycine may benefit sleep, memory, stroke recovery and heart health.
Let’s go over this more.
- Glycine Amino Acid: The Basics
- What Are the Benefits of Glycine?
- Glycine Foods: Natural Dietary Sources
- Glycine Supplement: Should You Take It?
- What Do They Use Glycine For?
Glycine Amino Acid: The Basics
Glycine, also known as aminoacetic acid, is the smallest and simplest amino acid. It was first isolated in 1820 and gets its name from the Greek word glykys, meaning ‘sweet,’ due to its taste.
Unlike some amino acids that must come from food, the body can make glycine from other compounds like serine and threonine. It makes up about one-third of collagen, the most abundant protein in the body, which is needed for skin, bones, tendons and ligaments. Glycine also contributes to the production of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant, and creatine, which supplies energy to muscles.
What Does Glycine Do in the Body?
So, what is the main function of glycine?
Glycine serves as one of the body's fundamental building blocks with multiple important roles. This amino acid acts as a key component in protein creation, particularly for collagen, which maintains the structure of skin, bones and connective tissues. Glycine also functions as a neurotransmitter, helping regulate nerve signals in the brain and spinal cord. What’s more, it supports detoxification by binding to harmful substances for elimination.
The body produces glycine naturally, but dietary sources and supplements can improve its availability for these essential processes.
Some studies suggest glycine may help with conditions like schizophrenia, heart disease and stroke recovery, though more research is needed, especially since some show the opposite for the latter. Glycine’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties further make it a substance that’s great for your health.

What Are the Benefits of Glycine?

Glycine for Sleep: How It Helps
Glycine has a calming effect on the brain, making it beneficial for sleep. It lowers core body temperature, a key factor in initiating restful sleep and helps with deeper non-REM sleep.
Studies show that taking glycine before bed can reduce the time it takes to fall asleep and improve overall sleep quality. Unlike sedative sleep aids, glycine supports natural sleep cycles without causing grogginess. While much of the research has been conducted on animals, preliminary human trials suggest similar benefits, making glycine a promising option for those struggling with insomnia or poor sleep.
Further Reading: Your Guide to How to Sleep Well at Night
Cognitive and Mental Health Benefits of Glycine
Glycine influences brain function by regulating neurotransmitters, including serotonin, which boosts mood and memory. Some studies indicate it may help reduce symptoms of schizophrenia when used alongside antipsychotic medications, though, as mentioned above, results are mixed.
Glycine’s ability to support glutathione production also protects brain cells from oxidative stress, potentially lowering the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Also, glycine’s role in nerve signalling may improve focus and mental clarity. While more research is needed, glycine shows potential as a natural supplement for cognitive support and mental well-being.
Glycine’s Role in Muscle Growth and Recovery
As a major component of collagen, glycine is needed for maintaining muscle, tendon and joint health. It’s used in muscle repair and reduces wasting, particularly in ageing or illness-related muscle loss.
Glycine is also used in creatine creation, which supplies energy for short, intense bursts of exercise. Some research suggests that glycine supplementation may improve muscle protein retention and recovery after physical exertion. While not as potent as branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) for direct muscle building, glycine supports overall tissue repair and resilience, making it valuable for athletes and active individuals.
How Glycine Supports Collagen Production
Collagen, the most abundant protein in the body, relies heavily on glycine for its structure.
About one-third of collagen's composition consists of glycine molecules arranged in repeating sequences. This amino acid provides the flexibility and strength needed for tissues like skin, tendons, cartilage and bones to maintain their integrity. Without enough glycine, collagen production slows, potentially leading to weaker joints, slower wound healing and reduced skin elasticity.
Supplemental glycine may support collagen synthesis, particularly as natural production declines with age.
Glycine’s Role in Detoxification and Digestion
Glycine plays an important part in the body's detoxification processes. It binds to toxins, including certain drugs and metabolic waste products, helping the liver neutralise and eliminate them efficiently. This function is particularly important for processing alcohol and other harmful substances that can strain liver function.
Glycine also contributes to bile acid production, which helps with fat digestion and nutrient absorption. Some research suggests glycine supplementation may protect against alcohol-related liver damage by improving metabolic clearance, though human studies are needed to confirm these effects.
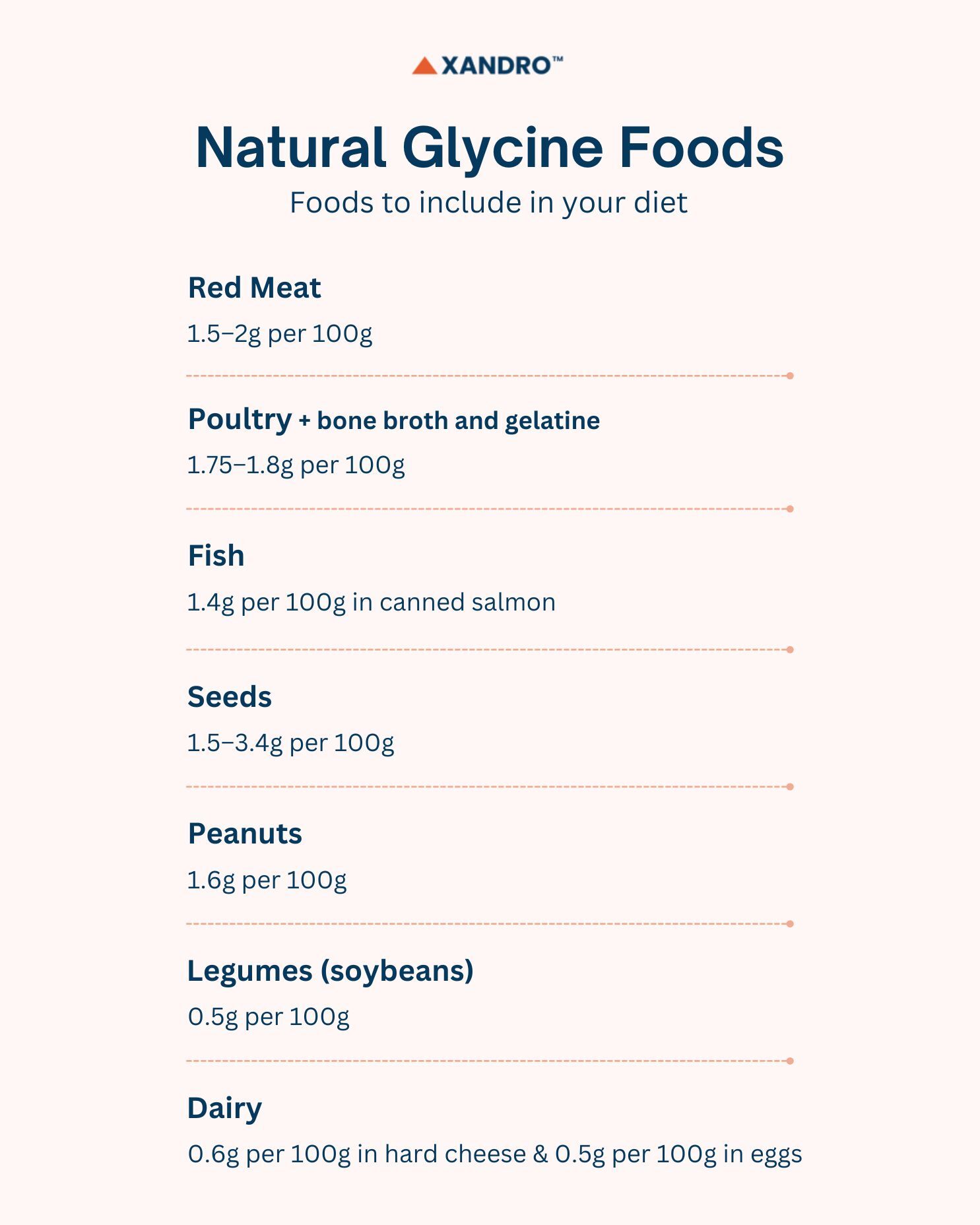
Glycine Foods: Natural Dietary Sources
Glycine occurs naturally in many protein-rich foods, offering an easy way to boost your intake through diet. While the body produces glycine on its own, consuming glycine-rich foods can support collagen formation, muscle recovery and overall health. Animal products typically contain the highest amounts due to their protein content, but plant-based sources also contribute to daily intake.
High-Glycine Foods to Include in Your Diet
Glycine Supplement: Should You Take It?
Glycine supplements may be great for those looking to improve their sleep, cognitive function, or collagen support.
While the body produces glycine naturally, supplementation can help individuals with specific needs, such as athletes requiring muscle recovery or people experiencing sleep difficulties. As mentioned above, glycine may support serotonin production, detoxification and heart health.
Before you start taking a pure glycine supplement, have a chat with your doctor to see if it’s right for you, especially for pregnant women, children, or those taking medications like antipsychotics. Most people tolerate glycine well, with possible mild side effects like nausea or stomach discomfort at higher doses.
Further Reading: The Difference Between Magnesium Glycinate vs Magnesium Bisglycinate
How Much Glycine Per Day Is Safe?
Typical glycine doses range from 2–5g daily for general health benefits. Studies on sleep improvement often use 3g taken before bedtime. Higher doses up to 30g have been used in research for specific conditions like schizophrenia, but such amounts should only be taken under medical supervision, as at these doses, opposing data has been found.
The body efficiently processes glycine, making toxicity rare at normal supplemental doses. Starting with smaller amounts (1–2g) and gradually increasing allows you to determine your tolerance while minimising potential digestive discomfort.
Further Reading: How Much Magnesium Glycinate Per Day?
Magnesium Glycinate: A Powerful Combo
Magnesium glycinate combines magnesium with glycine, creating a supplement that promotes relaxation and muscle recovery. The glycine component improves magnesium absorption while providing its calming effects on the nervous system. This form is particularly beneficial for those wanting better sleep quality, stress reduction, or muscle relaxation.
Unlike other magnesium forms that may cause digestive issues, magnesium glycinate is gentle on the stomach while delivering both mineral and amino acid benefits.
That’s why it’s added to our magnesium supplement: Magnesium Glycinate 500mg!
Who Should Avoid Glycine?

What Do They Use Glycine For?
What is Glycine Used For? Medical and Therapeutic Uses
Glycine has multiple therapeutic purposes in modern medicine and health supplementation.
Clinicians sometimes recommend glycine to support stroke recovery by helping regulate glucose metabolism and reduce inflammatory responses in the brain. Psychiatric applications include adjunct treatment for schizophrenia, where glycine may help manage symptoms when combined with antipsychotic medications.
The amino acid shows promise for improving sleep quality by regulating body temperature and circadian rhythms. Medical professionals also use glycine in bladder irrigation solutions during urological procedures to prevent blood clot formation. Emerging research further explores its potential for protecting against alcohol-induced liver damage and supporting metabolic health in type 2 diabetes.
Glycine in Skincare and Anti-Ageing
As collagen's primary structural component, glycine plays an important role in maintaining skin elasticity and youthfulness. The amino acid constitutes approximately one-third of collagen's molecular structure, supporting skin's ability to retain moisture and resist wrinkle formation.
Topical glycine formulations help promote wound healing and tissue repair in clinical settings for burns and ulcers. Oral glycine supplementation may boost collagen production from within, potentially reducing visible signs of ageing when combined with other collagen-supporting nutrients. Some skincare products add glycine for its hydrating properties and ability to support the skin's natural barrier function against environmental stressors.
End Note
Glycine is a versatile amino acid with benefits ranging from better sleep and mood to joint and heart health. It helps build collagen, detox the body and may even support brain function. While foods like meat, fish and seeds provide glycine, supplements can help fill gaps, especially for sleep support or muscle recovery.
For an extra boost, Xandro Magnesium Glycinate combines glycine with magnesium for deeper relaxation, improved sleep and muscle recovery. Just remember: If you have schizophrenia, low blood pressure, or diabetes, check with a doctor first. Stick to recommended doses (usually 2–5g/day) and enjoy the benefits of this simple yet powerful nutrient!
