Magnesium Wars: Magnesium Glycinate vs Magnesium Taurate
15th Apr 2025
Magnesium Glycinate vs Magnesium Taurate: Which One Is Right for You?
Magnesium is a powerhouse mineral involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, from muscle function and nerve signalling to heart health and bone strength. Yet, with so many different types of magnesium supplements available, choosing the right one can be incredibly confusing.
Two of the most popular forms are magnesium glycinate and magnesium taurate. Both are highly bioavailable and well-tolerated, but they serve slightly different purposes.
So, ‘What type of magnesium should I take?’ Keep on reading to learn more!
Further Reading: The Different Forms of Magnesium
What’s the Difference Between Magnesium Glycinate and Magnesium Taurate?
To begin, here’s a quick overview of the two before we dive deeper into them:
|
Feature |
Magnesium Glycinate |
Magnesium Taurate |
|
Key Component |
Magnesium + glycine (an amino acid) |
Magnesium + taurine (an amino acid) |
|
Best For |
Sleep, anxiety, stress, muscle relaxation |
Heart health, blood pressure, blood sugar regulation |
|
Absorption |
Highly bioavailable, gentle on digestion |
Well-absorbed, supports cardiovascular function |
|
Side Effects |
Rare (may cause mild nausea in some) |
Rare (possible dizziness or cramping) |
|
Who Should Avoid? |
People with kidney issues (in high doses) |
Those with low blood pressure or on heart medications (consult a doctor) |
So, which is better, magnesium glycinate or magnesium taurate?
Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate is magnesium bound to glycine, an amino acid known for its calming effects on the brain.
How Magnesium Glycinate Works in the Body
Magnesium glycinate is a chelated form, meaning magnesium is bound to glycine for better absorption. When you take it, a few things happen in your body:
- Rapid Absorption: The glycine molecule helps magnesium bypass the gut, reducing laxative effects.
- Crosses the Blood-Brain Barrier: Glycine acts as a neurotransmitter, promoting relaxation.
- Supports GABA Activity: This calming neurotransmitter helps reduce anxiety and improve sleep.
A study found glycine improves sleep quality by lowering core body temperature. What’s more, Research suggests magnesium glycinate may help depression by modulating serotonin.
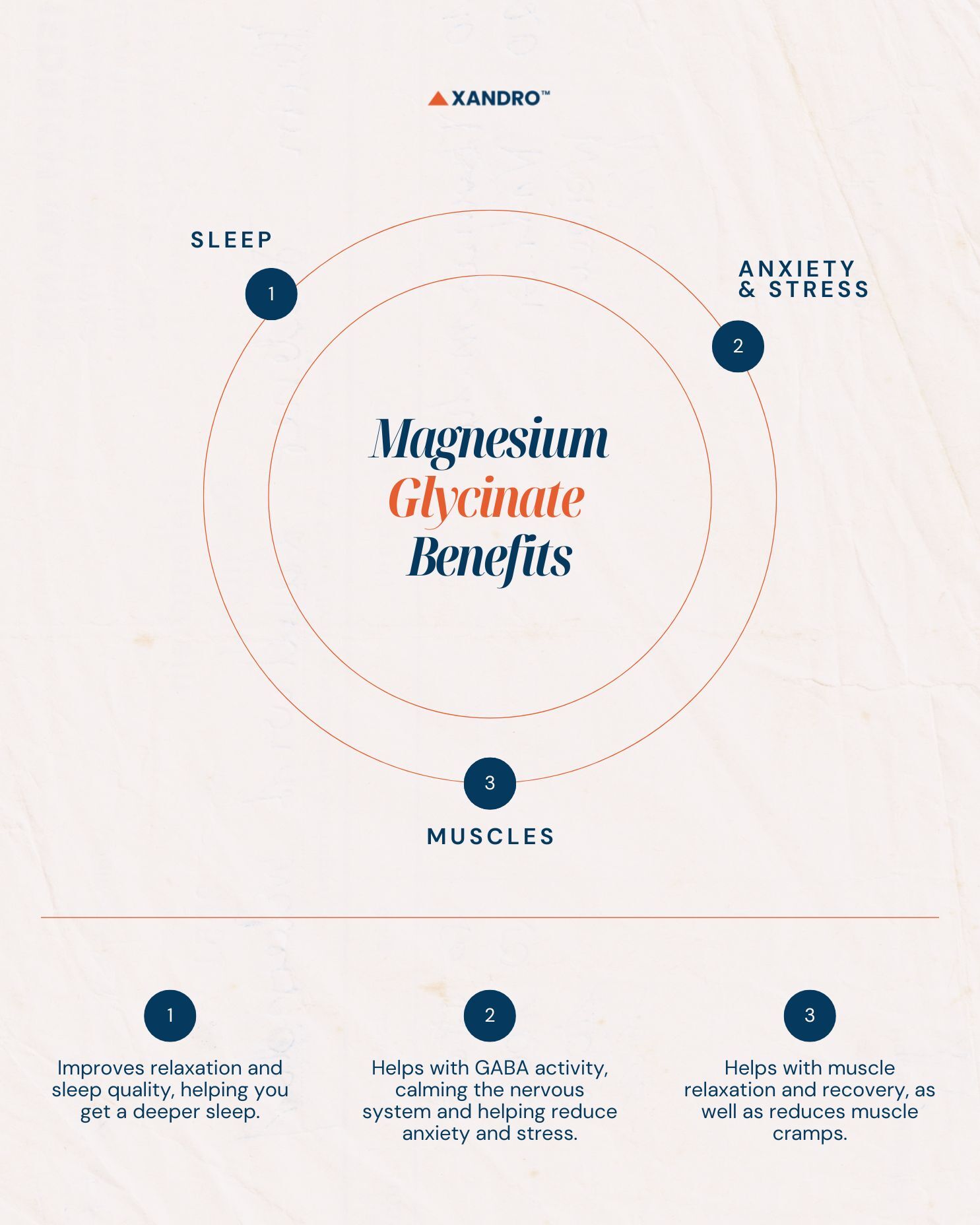
Key Magnesium Glycinate Benefits:
- Helps with deep sleep: Glycine improves relaxation and sleep quality.
- Reduces anxiety & stress: Helps with GABA activity, a neurotransmitter that calms the nervous system.
- Gentle on digestion: Unlike magnesium oxide or citrate, glycinate rarely causes diarrhoea.
- Muscle recovery: Helps with muscle relaxation and reduces cramps.
Further Reading: 7 Magnesium Glycinate Benefits
Who Should Take Magnesium Glycinate?
- People with insomnia or poor sleep quality.
- Those dealing with chronic stress, anxiety or depression.
- Individuals with digestive sensitivities (since it doesn’t cause laxative effects).
Who Should Not Take Magnesium Glycinate?
- Those with severe kidney disease (excess magnesium can be harmful).
- Those on sedatives or antidepressants (glycine may enhance effects).
- While rare, magnesium glycinate side effects may include mild nausea and drowsiness (if taken in high doses during the day)
Best Time to Take Magnesium Glycinate
- 30–60 inutes before bed: Helps you get a deeper sleep.
- With meals: Reduces potential stomach upset.
Magnesium Taurate
Magnesium taurate combines magnesium with taurine, an amino acid that helps with heart and metabolic health.
How Magnesium Taurate Works in the Body
Magnesium taurate combines magnesium with taurine, a conditionally essential amino acid needed for:
- Cardiovascular Function: Taurine regulates calcium in heart cells, preventing arrhythmias.
- Insulin Sensitivity: Helps glucose enter cells more efficiently.
- Neuroprotection: Shields brain cells from oxidative stress.
A 2018 animal study showed it reduced blood pressure in hypertensive rats. Taurine deficiency is linked to cardiomyopathy (heart muscle disease). It also may protect against diabetes by improving insulin response.
Key Magnesium Taurate Benefits:
- Helps you keep a healthy blood pressure: Studies suggest taurine helps regulate blood pressure.
- Protects heart function: May reduce oxidative stress on the heart.
- Balances blood sugar: Taurine improves insulin sensitivity.
- Neuroprotective effects: May help with brain recovery after injury.
Further Reading: Magnesium vs Melatonin: Which is Better for Sleep?
Who Should Take Magnesium Glycinate?
- People with high blood pressure or heart palpitations.
- Those at risk of diabetes (taurine supports glucose metabolism).
- Individuals recovering from stress-related fatigue or migraines.
Who Should Not Take Magnesium Taurate?
- People with already low blood pressure (taurine may lower it further).
- Those on blood pressure medications (may cause excessive lowering).
- People with bradycardia (very slow heart rate).
- Those on heart medications (speak with a doctor first).
- While rare, magnesium Taurate side effects may include low blood pressure (if already hypotensive) and mild dizziness.
Best Time to Take Magnesium Taurate
- Morning or early afternoon: Helps with energy and heart function.
- Post-workout: Helps with muscle recovery and electrolyte balance.

FAQs
Is Magnesium Glycinate or Taurate Good for Heart Palpitations?
Magnesium taurate is often recommended for heart palpitations because taurine helps regulate heart rhythm, while magnesium prevents electrolyte imbalances that trigger palpitations. Magnesium glycinate may also help if palpitations are stress-related, though.
Is Magnesium Glycinate Better Than Taurate?
It depends on your needs:
- For sleep, anxiety and stress → Magnesium glycinate is the better choice.
- For heart health, blood pressure and blood sugar → Magnesium taurate is more effective.
Both are excellent forms of magnesium, but their amino acid partners (glycine vs taurine) give them unique benefits.
Can I Take Magnesium Taurate and Glycinate Together?
Combining magnesium glycinate and magnesium taurate can provide both calming and cardiovascular benefits. Just make sure that you stick to the recommended daily intake (310–420mg for most adults). If taking high doses, speak with your doctor first to make sure you’re avoiding excess magnesium intake.
Further Reading: What Does Magnesium Do for Your Muscles?
Which is Better, Magnesium Taurate or Glycinate, for Specific Conditions?
|
Condition |
Best Magnesium Form |
Why? |
|
Insomnia |
Glycinate |
Glycine promotes deep sleep |
|
Anxiety/Stress |
Glycinate |
Boosts GABA, calms nerves |
|
High Blood Pressure |
Taurate |
Taurine regulates heart rhythm |
|
Heart Palpitations |
Taurate |
Stabilises electrical heart activity |
|
Diabetes/Blood Sugar |
Taurate |
Improves insulin sensitivity |
|
Muscle Cramps |
Glycinate |
Relaxes muscles effectively |
|
Migraines |
Both (taurate may be better) |
Taurine reduces neuroinflammation |
End Note
So, which magnesium should you take?
If you’re looking for better sleep, relaxation, stress and anxiety relief and muscle cramps and recovery relief, choose magnesium glycinate. For heart health, blood pressure and blood sugar balance, choose magnesium taurate.
Whether you choose magnesium glycinate or taurate, both are excellent options that go beyond basic magnesium supplementation. Glycinate helps you unwind, while taurate keeps your heart in check.
Both are high-quality, absorbable forms, so the best choice depends on your health goals. Just make sure you speak with your doctor before you begin taking them.
If you think that magnesium glycinate is the best form of magnesium for you, check out Xandro’s Magnesium Glycinate 500mg, designed to improve you sleep and support your muscles.
You can read about our comparisons of the other different kinds of magnesium supplements here to find out what is the best form of magnesium to take for you.
